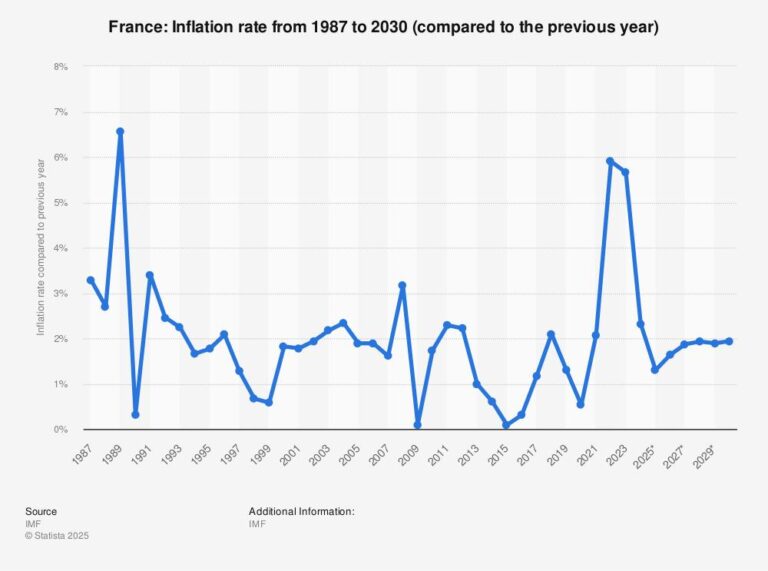
In a testament to its resilient economy, France has managed to contain inflation to below 1%, despite ongoing challenges in the global energy markets. According to recent data reported by Bloomberg.com, the country’s persistent struggles with energy prices continue to exert downward pressure on consumer costs. As European nations grapple with inflationary pressures spurred by geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions, France’s ability to maintain such low inflation figures raises questions about the effectiveness of its economic policies and the potential implications for future growth. This article explores the factors influencing France’s inflation landscape and the broader context of energy market impacts on the economy.
France’s Inflation Trends: Analyzing Persistent Low Rates Amid Global Pressures
France has experienced remarkably low inflation rates, consistently staying below 1% despite various global economic pressures. This trend defies expectations as many countries grapple with rising prices, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions. Analysts attribute France’s stability largely to a combination of governmental measures and energy sector dynamics, which have helped insulate consumers from sharper spikes in costs. As the European energy market stabilizes, the impact of fluctuating oil and gas prices remains a focal point for policymakers.
Key factors contributing to this persistence include:
- Controlled energy prices: Recent government interventions have aimed at capping energy costs, significantly alleviating inflationary pressures.
- Strong food supply management: A sustained agricultural output has helped maintain food prices, curbing them in an environment where many nations face escalating costs.
- Consumer behavior: A cautious consumer sentiment, driven by economic uncertainty, has resulted in decreased demand for non-essential goods, further stabilizing prices.
| Month | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| January | 0.8 |
| February | 0.9 |
| March | 0.7 |
Moving forward, economists will be closely monitoring the implications of external economic factors, particularly how shifts in energy markets could influence these low inflation rates. The resilience of France’s economy serves as a case study in effective policy responses, showcasing how targeted interventions can lead to sustained price stability amidst global volatility.
Energy Costs and Their Impact: Understanding the Relationship Between Prices and Economic Stability
The recent data from France indicates a persistent trend where inflation continues to remain below 1%, largely attributed to the stagnant energy prices. This scenario highlights the profound impact that energy costs exert on overall price levels, influencing consumer behavior and economic growth. Analysts suggest that lower energy rates have shielded the economy from more substantial inflation, contributing to a delicate equilibrium that fosters both stability and uncertainty. The correlation between energy prices and inflation will be crucial for policymakers as they navigate the complexities of economic recovery in an ever-evolving landscape.
While low energy costs can act as a buffer against inflation, they also present a dual-edged sword. On one hand, consumers benefit from more affordable heating and transportation expenses, enhancing disposable income. On the other hand, prolonged low prices can undermine investment in vital infrastructure and lead to job losses in the energy sector. As illustrated in the table below, fluctuations in energy prices can trigger significant shifts in various economic indicators, effectively serving as a barometer for economic stability.
| Year | Average Energy Price (€) | Inflation Rate (%) | Consumer Spending Growth (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 90 | 0.5 | 1.2 |
| 2021 | 85 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| 2022 | 80 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
Consumer Confidence in a Low-Inflation Environment: Strategies for Maintaining Spending
As France continues to experience low inflation rates, hovering below 1%, consumer confidence is gradually taking a positive turn. This environment offers unique opportunities for various sectors, encouraging innovative strategies to maintain spending among consumers. Retailers and service providers can leverage this market condition by focusing on enhancing the customer experience through tailored offerings. Key strategies include:
- Promotional Campaigns: Targeted discounts and loyalty programs can create incentives for spending.
- Value-Added Services: Offering complementary services can enhance perceived value without significantly raising prices.
- Consumer Education: Informing consumers about the advantages of spending now can help stimulate demand.
Moreover, businesses must remain vigilant and adaptable to shifts in consumer behavior amid different economic conditions. Continuous market research and feedback collection can empower companies to pivot their strategies effectively. Here are some factors influencing consumer spending that businesses should monitor:
| Factor | Impact on Spending |
|---|---|
| Energy Prices | Decrease in disposable income may lead to reduced spending on non-essential goods. |
| Employment Trends | Higher employment typically boosts consumer confidence and spending. |
| Consumer Sentiment | Positive sentiment correlates with increased spending, even in low-inflation scenarios. |
Policy Recommendations for Sustained Economic Growth: Navigating Challenges in the Energy Sector
The French economy is at a crucial juncture, with persistent challenges in the energy sector casting a shadow over efforts to maintain robust economic growth. Policymakers must consider a multi-faceted approach that integrates both immediate responses and long-term strategies. Diversifying energy sources will prove essential, particularly in light of fluctuating global prices and geopolitical tensions. Emphasizing renewable energy investments, such as solar and wind projects, could not only stabilize energy costs but also create jobs and stimulate local economies.
Moreover, implementing regulatory reforms to streamline the permitting of sustainable energy projects can encourage private investment and innovation. The government should also explore strategic partnerships with neighboring countries to enhance energy security, ensuring a collaborative approach to tackling energy supply challenges. In order to support consumers and businesses facing utility price hikes, temporary measures such as subsidies or tax breaks should be put in place. Below is a snapshot of potential policy instruments and their anticipated outcomes:
| Policy Instrument | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Tax Credits | Stimulate investment in green technologies |
| Energy Efficiency Grants | Reduce overall consumption and costs for households |
| Cross-Border Energy Agreements | Enhance energy security and price stability |
To Conclude
In conclusion, France’s inflation rate remaining below 1% underscores the significant impact of energy prices on the broader economic landscape. While pressure from global markets and external factors continues to pose challenges, the current stability in France presents a unique contrast to the inflationary trends seen in many other nations. Policymakers and economists will be watching closely as energy dynamics evolve, with the potential to shift this delicate balance. As the situation develops, France’s resilience in maintaining low inflation could serve as a case study for other economies navigating similar turbulent waters.