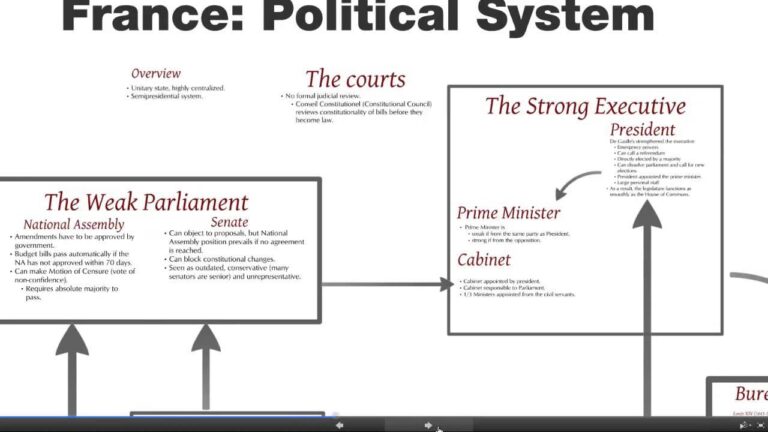
France’s political landscape is showing signs of significant strain, raising concerns about the stability and functionality of its institutions. In a recent analysis by the Financial Times, the creaking mechanisms of governance have come under scrutiny as the nation grapples with economic challenges, social unrest, and a polarized political climate. As President Emmanuel Macron navigates complex legislative hurdles and public discontent, the resilience of France’s political framework is increasingly questioned. This article delves into the enduring structural tensions and the implications for governance in a country long regarded as a pillar of European democracy. With mounting pressures from various fronts, the future of France’s political institutions hangs in the balance, prompting a critical assessment of their ability to adapt and respond to the demands of a changing society.
The Erosion of Democratic Norms in France’s Government
The current landscape of France’s political institutions reveals a concerning trend: a gradual weakening of democratic practices that were once the cornerstones of its governance. As citizen disengagement grows, many observers argue that the checks and balances meant to uphold democratic integrity are increasingly under threat. The following factors are contributing to this erosion:
- Institutional Polarization: The rise of extreme political factions has led to heightened partisanship, making bipartisan cooperation challenging.
- Executive Overreach: A tendency for the executive branch to bypass parliamentary procedures has raised alarms regarding accountability.
- Media Controls: Heightened scrutiny and pressure on independent media organizations diminish the public’s access to unbiased information.
Recent national policies have also sparked debate about the limits of democratic discourse, with many fearing that these changes could set dangerous precedents. An examination of government actions highlights the shifting dynamics:
| Year | Government Action | Impact on Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Implementation of state emergency laws | Restricted civil liberties |
| 2020 | Increased surveillance measures | Threatened privacy rights |
| 2023 | Restrictions on protest activities | Undermined public dissent |
Challenges to Legislative Effectiveness Amid Growing Discontent
As the discontent among citizens reaches new heights, France’s political system faces hurdles that hinder its ability to respond effectively to the challenges at hand. Protests, social movements, and a general distrust in governmental institutions have become commonplace, creating an overwhelming sentiment that lawmakers are out of touch with the populace. This disconnect is compounded by a fragmented political landscape, where the proliferation of parties leads to ineffective coalitions and further stalemates in decision-making. With such divisions, it becomes increasingly difficult for leaders to chart a clear course that addresses urgent societal issues.
Moreover, the legislative process is stymied by a lack of public confidence, which can lead to populist movements gaining traction and shifting the narrative away from traditional governance. The ensuing ambiguity creates an environment ripe for political opportunism, where party agendas overshadow collaborative efforts aimed at governance. Lawmakers are thus left grappling with disparate factions within their own ranks, leading to prolonged debates over essential reforms. The table below highlights recent legislation and their reception, illustrating the chasm between parliamentary actions and public sentiment:
| Legislation | Objective | Public Support (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Pension Reform | Raise retirement age | 32% |
| Tax Cuts | Reduce income tax | 45% |
| Environmental Policy | Increase green energy | 65% |
Strengthening Accountability in France’s Political Landscape
In a time marked by mounting public discontent and political turbulence, the need for enhanced accountability within French institutions has never been more critical. The historical legacy of France’s political structure, deeply rooted in both tradition and nationalism, faces scrutiny as citizens demand transparency and reliability from their leaders. Amid increasing pressures from grassroots movements and a disillusioned electorate, the government must adapt by implementing robust frameworks that can restore trust. Efforts to establish clear lines of responsibility and an emphasis on ethical governance are essential for fostering a political culture that is both responsive and responsible.
Key measures to strengthen accountability may include:
- Regular Audits: Instituting mandatory audits of public funds and spending can deter corruption and misuse of resources.
- Enhanced Public Disclosure: Ensuring politicians declare their assets and potential conflicts of interest can provide vital information to the electorate.
- Citizen Panels: Establishing citizen review panels to evaluate governmental actions encourages participatory democracy and empowers voters.
Furthermore, the introduction of technology-driven solutions, such as accessible online platforms for tracking political expenditures and performance metrics, can significantly elevate the standards of accountability. The challenge lies not only in policy reform but also in fostering a culture that values integrity and serves as a deterrent to malpractice. By embracing these strategies, France can rejuvenate its political institutions to meet the expectations of a modern democracy.
Recommendations for Revitalizing Civic Engagement and Institutional Resilience
To foster a more engaged citizenry and bolster institutional resilience, several strategic initiatives can be implemented. It is essential to harness digital platforms to encourage participation, especially among younger demographics. By integrating interactive tools within existing civic platforms, authorities can create more avenues for dialogue and feedback. Additionally, promoting community-led initiatives will empower citizens to take ownership of local issues, fostering a culture of collaboration and accountability.
Furthermore, strengthening educational programs that focus on civic literacy is vital for instilling a sense of responsibility in future generations. Schools should integrate curricula that emphasize the importance of civic engagement and democratic practices. Likewise, public dialogues and forums should be organized regularly, allowing citizens to voice concerns and engage with policymakers directly. This can lead to innovative solutions tailored to community needs. A collaborative approach, prioritizing transparency and inclusivity, is critical for revitalizing trust in governmental institutions.
To Conclude
In conclusion, the current state of France’s political institutions highlights the fragility of a system grappling with growing discontent and systemic challenges. As the nation faces a series of crisesŌĆöfrom economic pressures to social unrestŌĆölawmakers must navigate an increasingly polarized landscape. The potential for reform remains, but without decisive action and public trust, France risks deepening the divides that threaten its foundational governance structures. As the political landscape evolves, the resilience of these institutions will be crucial in shaping the future of both the country and its citizens. Stakeholders must remain vigilant as they seek to address these urgent issues, ensuring that France can emerge stronger and more united in the face of adversity.