As Giorgia Meloni marks three years at the helm of ItalyŌĆÖs government, the spotlight turns to the state of the nationŌĆÖs economy under her leadership. Tasked with navigating a complex landscape marked by global uncertainties, domestic challenges, and evolving European dynamics, MeloniŌĆÖs administration has sought to steer Italy towards stability and growth. This article takes an in-depth look at the key economic developments since Meloni took office, examining the policies implemented, their impact on businesses and markets, and the outlook for ItalyŌĆÖs economic future.
ItalyŌĆÖs Economic Performance Under MeloniŌĆÖs Leadership
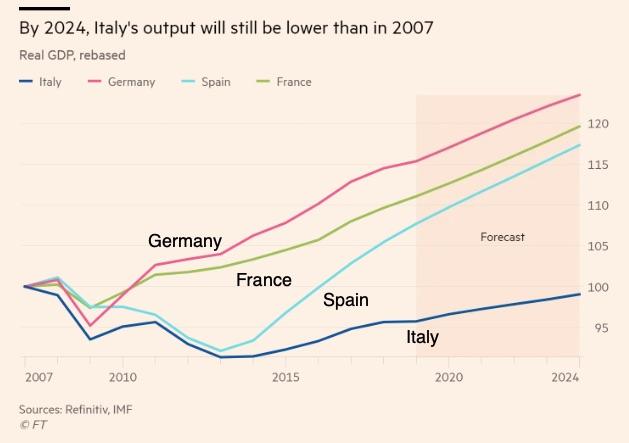
Since Giorgia Meloni assumed office, Italy’s economy has displayed a mix of resilience and caution against a backdrop of global uncertainty. Key sectors such as manufacturing and exports have benefited from targeted government incentives, while inflationary pressures, compounded by energy costs, have tempered consumer confidence. MeloniŌĆÖs administration prioritized fiscal prudence, balancing growth initiatives with the need to maintain EU commitments on deficit reduction. However, challenges remain, particularly in unemployment rates among youth and regional disparities that continue to shape the economic landscape.
Notable economic indicators from Meloni’s tenure include:
- GDP growth averaging around 1.2% annually, outperforming some southern European peers
- Unemployment rate fluctuating between 8.5% and 9.3%, with youth unemployment stubbornly high
- Public debt remaining above 130% of GDP, prompting ongoing debates on sustainability
| Indicator | 2019 | 2023 | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate | 0.3% | 1.2% | +0.9% |
| Unemployment Rate | 9.8% | 8.7% | -1.1% |
| Public Debt (% of GDP) | 134% | 131% | -3% |
| Inflation Rate | 0.6% | 7.9% | +7.3% |
Key Sectors Driving Growth and Challenges Ahead
Manufacturing and export sectors continue to be the backbone of Italy’s economic vitality, especially in the northern regions where industrial clusters thrive. Key industries such as automotive, fashion, and machinery have leveraged both traditional craftsmanship and innovation to capture significant global market shares. However, these sectors face mounting pressure from global supply chain disruptions and rising production costs, challenging their competitiveness amid evolving international dynamics.
Meanwhile, the services sector, particularly tourism and financial services, has experienced a cautious rebound following the pandemic downturn, contributing substantially to GDP growth. Yet, Italy’s labor market inefficiencies and regional disparities pose ongoing obstacles. Policymakers are urged to address structural reforms in education and infrastructure to bridge gaps between the prosperous north and the lagging south, fostering more inclusive economic development.
| Sector | 2023 Growth Rate | Main Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | +2.1% | Supply chain disruption |
| Tourism | +4.5% | Seasonal volatility |
| Financial Services | +1.7% | Regulatory constraints |
| Agriculture | +0.8% | Climate change impact |
Impact of Government Policies on Inflation and Employment
Italy’s government under Giorgia Meloni has implemented a mix of fiscal and regulatory measures intended to curb inflation without stifling employment growth. Targeted subsidies on energy prices and controlled public spending have helped moderate inflationary pressures, yet challenges remain due to global supply chain disruptions and rising commodity costs. The delicate balance of policy intervention seeks to protect the most vulnerable populations while maintaining investor confidence in the country’s economic stability.
On the employment front, recent policies aim to boost labor market participation by simplifying hiring procedures and extending incentives for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Below is a concise overview of some key policy impacts:
- Tax incentives: Encouraged SME hiring, particularly among youth and women.
- Vocational training programs: Improved workforce adaptability to evolving market demands.
- Minimum wage adjustments: Attempted to preserve purchasing power amid inflation.
- Public investment: Focused on infrastructure to stimulate job creation.
| Policy | Inflation Impact | Employment Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Energy subsidies | Reduced household energy bills | Stable consumption maintaining jobs |
| SME hiring tax breaks | Minimal direct effect | Increased employment rates |
| Job training schemes | Neutral | Improved job placement |
Strategic Recommendations for Sustained Economic Stability
To solidify Italy’s economic trajectory under Meloni’s leadership, a multi-faceted approach is crucial. Priority should be given to targeted investment in innovation and technology, fostering a competitive edge in key sectors such as manufacturing and green energy. Strengthening partnerships with European allies to leverage funding and expertise will enhance Italy’s capacity to modernize its infrastructure and digital ecosystems. Additionally, reforms aimed at simplifying bureaucracy can attract foreign direct investment and empower small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), the backbone of ItalyŌĆÖs economy.
Equally important is fiscal prudence combined with social inclusivity. Measures to broaden the tax base and improve compliance should be balanced with policies that support vulnerable populations, mitigating income inequality and boosting consumer confidence. The table below outlines key strategic pillars with corresponding focus areas:
| Strategic Pillar | Focus Area | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Innovation & Technology | R&D funding, digital infrastructure | Enhanced global competitiveness |
| Regulatory Reform | Bureaucracy reduction, SME support | Higher investment and job creation |
| Fiscal Policy | Tax base expansion, social programs | Balanced growth and social cohesion |
| European Cooperation | Funding access, policy alignment | Accelerated economic modernization |
To Wrap It Up
As Giorgia Meloni marks three years in office, Italy’s economy presents a complex portrait of resilience amid ongoing challenges. While strides have been made in areas such as employment and fiscal stability, structural issues and external pressures continue to test the government’s ability to deliver sustained growth. Observers and investors alike will be watching closely to see how Italy navigates the evolving economic landscape in the months ahead.