Introduction
As the digital landscape continues to expand, the Port of Marseille, a critical hub for trade and maritime activities, faces an unprecedented challenge. Increasingly, data centersŌĆöthe powerhouses of the internetŌĆöare setting up operations in the region, lured by its strategic location and robust infrastructure. However, these facilities come with a significant cost: an insatiable appetite for electricity that is straining local resources. In a recent report by EL PA├ŹS, the implications of this surge in energy consumption are brought to light, highlighting concerns over sustainability and the impact on the portŌĆÖs traditional functions. As local authorities grapple with balancing technological advancement and environmental responsibility, a pressing question emerges: can the Port of Marseille sustain its growth amid the mounting demands of the digital age?
Impact of Data Center Growth on Local Energy Resources
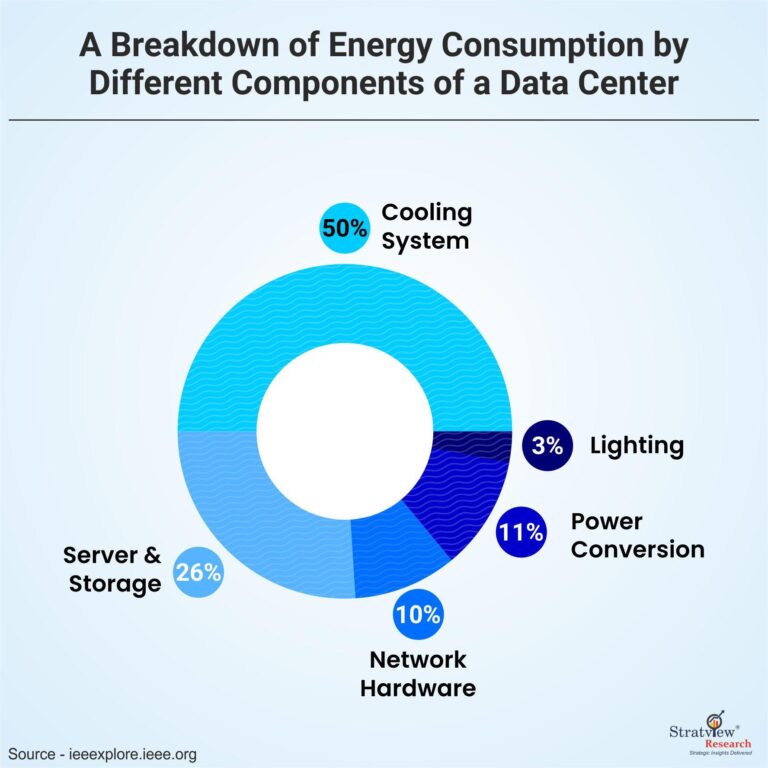
The rapid expansion of data centers around the Port of Marseille has raised significant concerns regarding local energy resources. These facilities are notorious for their intensive energy consumption, driven by the need to power servers, cooling systems, and other infrastructure crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. According to recent reports, data centers can consume more electricity than entire cities, placing immense pressure on regional power grids and limiting energy availability for residents and businesses alike. Key factors contributing to this escalating demand include:
- Increased reliance on digital services: As companies shift more operations online, demand for data processing has skyrocketed.
- Climate control systems: Sophisticated cooling systems are essential in maintaining optimal operating conditions, leading to excessive energy use.
- Frequent upgrades: The continuous push for state-of-the-art technology results in higher energy consumption.
Furthermore, there is a growing concern about the sustainability of this energy usage. Local authorities are grappling with the daunting task of balancing economic development with environmental considerations. The influx of data centers has prompted discussions on renewable energy investments and energy-efficient technologies, as communities seek to mitigate the adverse effects. The impact can be broken down into several key areas:
| Impact Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Resource Strain | Significant drain on local electricity supplies, risking outages. |
| Cost Implications | Potential increase in electricity prices for local consumers. |
| Environmental Concerns | Increased carbon footprint due to fossil fuel dependency for energy. |
Environmental Consequences of Increased Electricity Demand
The soaring demand for electricity, particularly driven by the proliferation of data centers, poses severe environmental challenges that are often overlooked. As these facilities expand, they consume astounding amounts of power, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The energy-intensive operations not only place strain on local grids but also exacerbate the already critical situation of energy sustainability. In cities like Marseille, where these centers are emerging, the competition for resources can lead to adverse effects, including potential energy shortages for local communities and increased energy prices.
Moreover, increased electricity consumption has direct implications for water resources, as many power generation processes require substantial water for cooling. The phenomenon often leads to water scarcity and affects local ecosystems. In addition, the reliance on fossil fuels to meet these growing energy needs further complicates the climate crisis. As stakeholders grapple with these systemic issues, it becomes crucial to explore renewable energy solutions and implement energy-efficient technologies that can mitigate the environmental toll of data centers without stifling technological advancement.
Strategies for Sustainable Data Center Development
In the face of escalating energy consumption and environmental concerns, the development of data centers requires innovative strategies aimed at sustainability. Stakeholders must prioritize renewable energy sources to power operations. By harnessing wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, facilities can significantly reduce their carbon footprints. Moreover, implementing energy-efficient technologies, such as advanced cooling systems and virtualization techniques, can optimize resource allocation while minimizing waste.
Collaboration between local governments and data center operators is essential to promote eco-friendly development. Creating incentives for using green building materials and establishing guidelines for water and energy usage can foster a more sustainable environment. Furthermore, implementing circular economy principlesŌĆöwhere waste products are repurposed within the industryŌĆöcan lead to more resilient infrastructures. By adopting these strategies, stakeholders can ensure the longevity of both data center operations and the ecosystems they impact.
Policy Recommendations for Balancing Economic Growth and Resource Management
The rapid expansion of data centers in Marseille has brought to light the urgent need for comprehensive policies aimed at balancing economic pursuits with sustainable resource management. As these digital infrastructures continue to thrive, policymakers must prioritize the integration of energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources. This can be achieved through measures such as:
- Incentivizing renewable energy adoption: Offering subsidies for data centers that utilize solar, wind, or other renewable energy sources.
- Implementing strict energy efficiency standards: Mandating energy-saving technologies in the construction and operation of data centers.
- Encouraging academic and industry partnerships: Fostering collaboration for innovative solutions focused on sustainable energy use.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks should encourage data center operators to invest in water conservation measures to mitigate adverse impacts on local water supplies. Strategies may include:
- Establishing water usage quotas: Setting limits on water consumption that align with local availability.
- Utilizing advanced cooling systems: Encouraging the adoption of technology that minimizes water usage while ensuring optimal operating temperatures.
- Conducting regular environmental impact assessments: Mandating evaluations of resource utilization and its effects on surrounding communities.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, the increasing demand for data centers at the Port of Marseille underscores a critical intersection between technological advancement and environmental sustainability. As these facilities continue to expand, the strain on the region’s electricity resources poses significant challenges for both local authorities and residents. While the benefits of a digitally connected world are undeniable, the implications of high energy consumption must not be overlooked. Stakeholders are urged to pursue innovative solutions to balance economic growth with ecological responsibility. The future of the Port of Marseille hinges on this delicate equilibriumŌĆöone that will determine not only the portŌĆÖs role in the digital age but also its commitment to environmental stewardship. As this situation evolves, it will be crucial to monitor how policy decisions shape the interaction between technology and ecological sustainability in the years to come.